Overview
CERID’s studies aim to define the virus and host components that control HCV infection outcome and liver disease.
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a blood-borne virus. Today, the most common way people get infected is by needle sharing during intravenous drug use.
This virus causes chronic (long-term) infection in 75%-85% of infected people, often leading to chronic liver disease, including cirrhosis and liver cancer.
The symptoms of liver damage may not appear for several years. Therefore, it is important for people at high risk of infection to be tested for Hepatitis C so they can start treatment as early as possible.
Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
OUR FOCUS
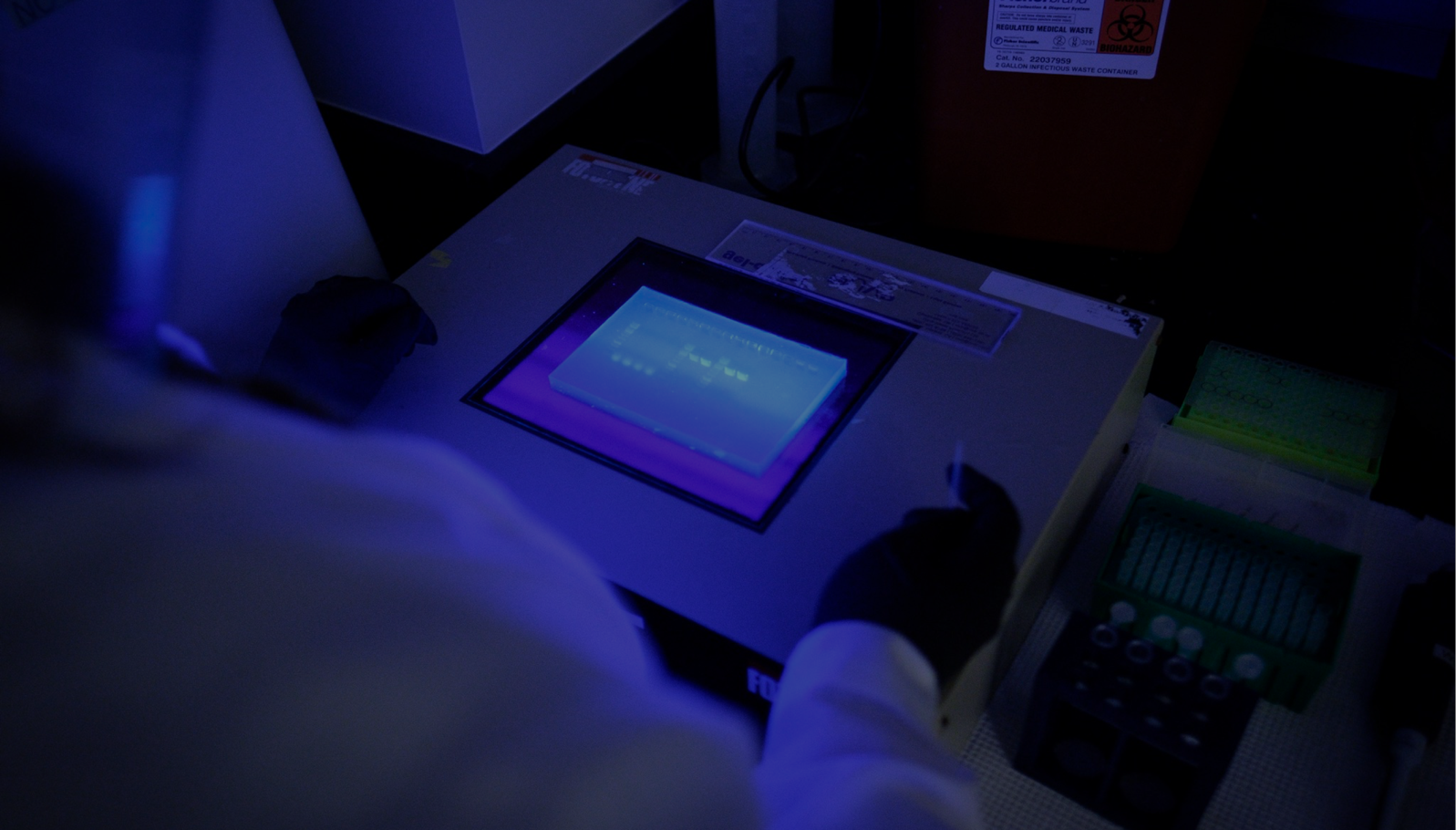
CERID is studying the use of reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for detection of Babesia microti parasites.
Associated labs