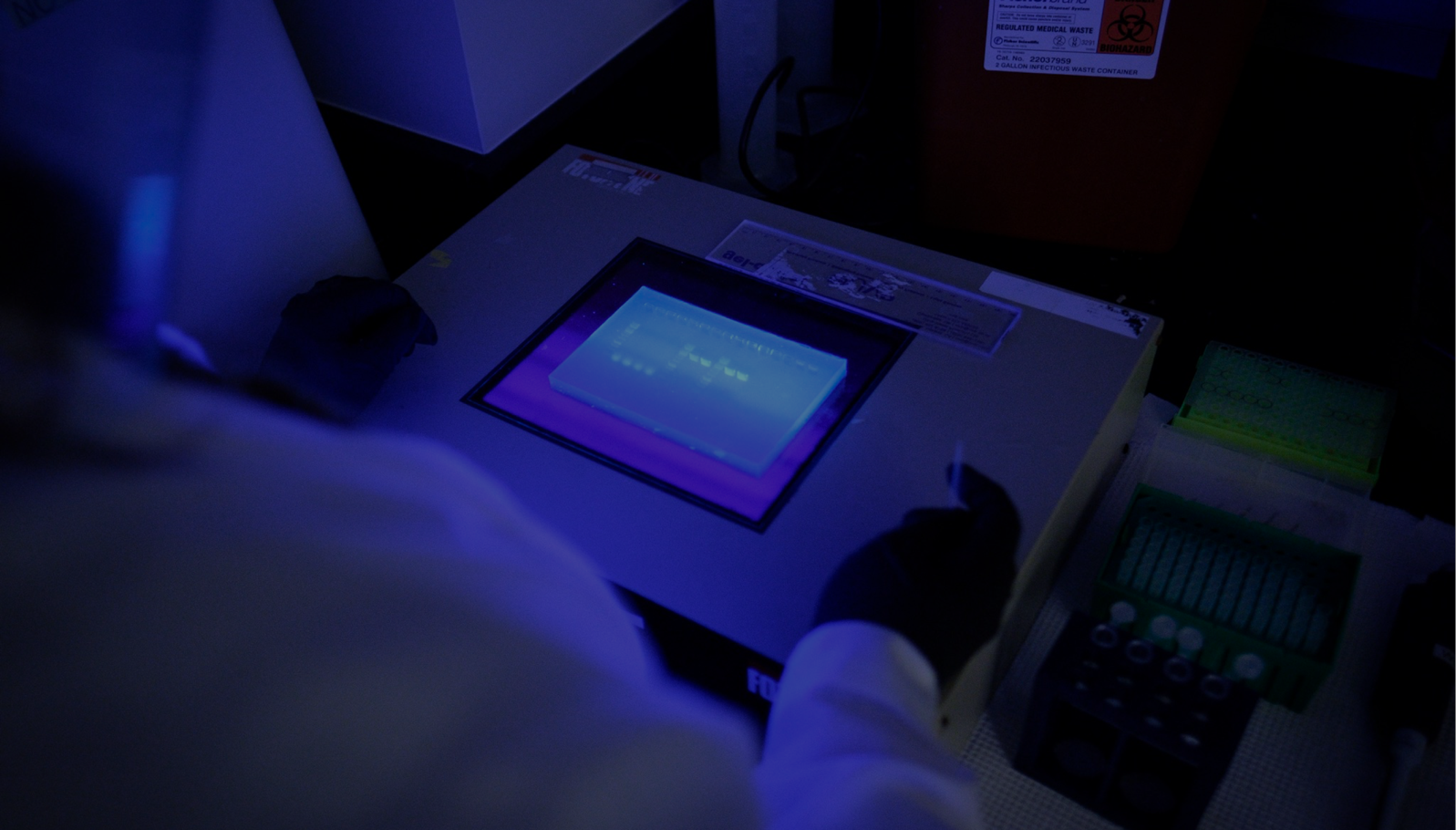
Overview
The Staphylococcus genus includes at least 30 species. Most are harmless and reside normally on the skin and mucous membranes of humans and other organisms. Found worldwide, they are a small component of soil microbial flora.
Several species can cause a wide variety of infections in humans and other animals through infection or the production of toxins. Staphylococcal toxins are a common cause of food poisoning. Staphylococci can also cause bacterial conjunctivitis.
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a bacterium responsible for several difficult-to-treat infections in humans. MRSA is any strain of Staphylococcus aureus that has developed resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics, which include the penicillins and the cephalosporins.
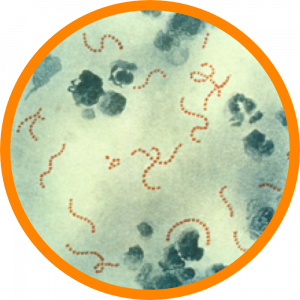
Streptococcus (Strep) has 2 types – group A and group B. Group A strep causes strep throat, scarlet fever, impetigo, toxic shock syndrome and cellulitis & necrotizing fasciitis.
Group B strep can cause blood infections, pneumonia and meningitis in newborns. In adults, it can cause urinary tract infections, blood infections, skin infections and pneumonia.
Antibiotics are used to treat strep infections.
Source: MedlinePlus, Centers for Disease Control: Group A Strep, Group B Strep
Associated labs