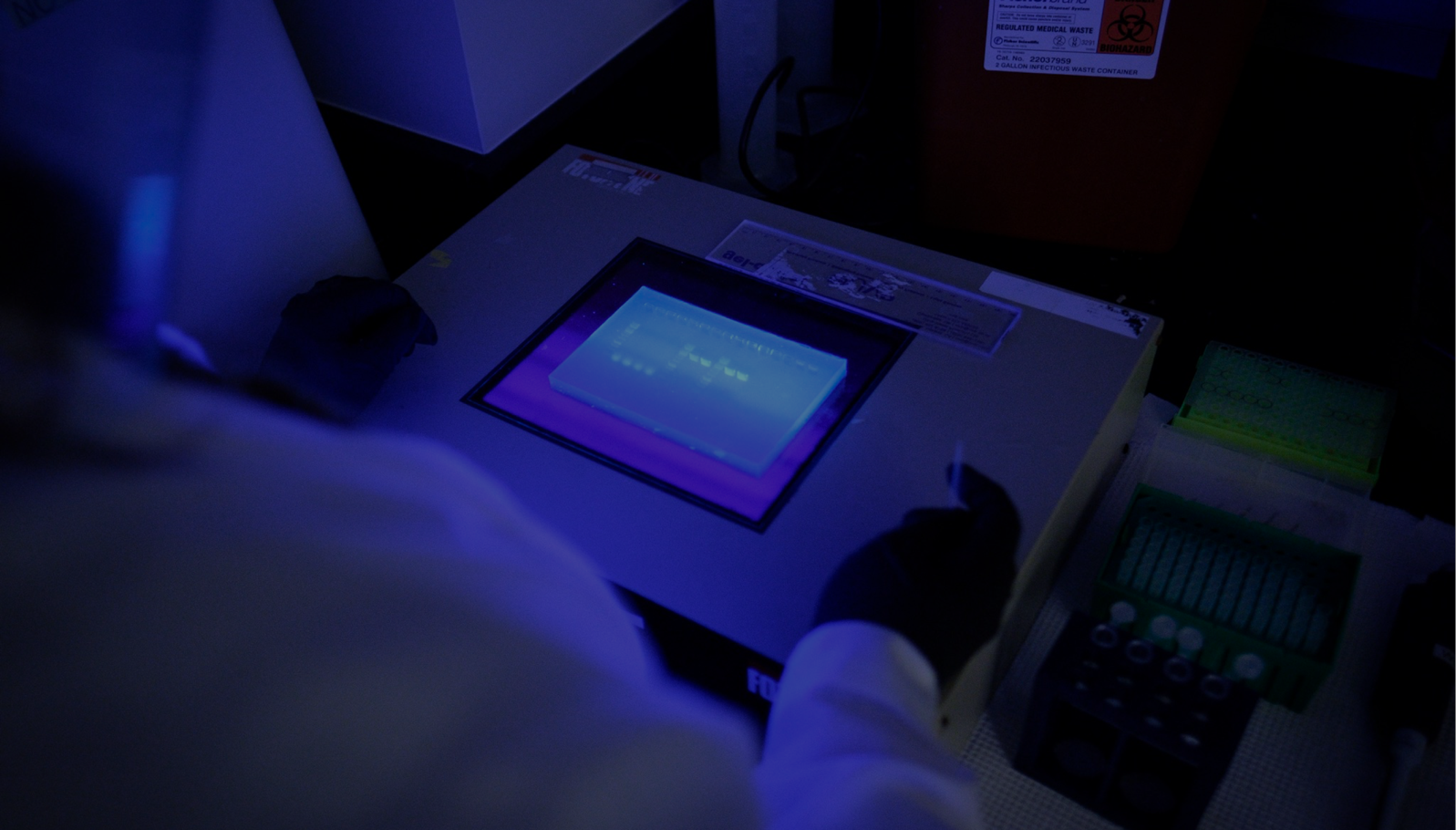
Overview
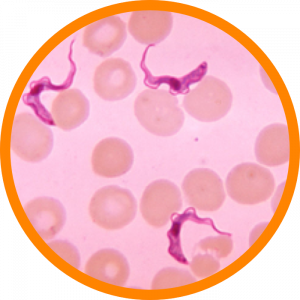 Human African trypanosomiasis is caused by protozoa of the species Trypanosoma brucei and transmitted by the tsetse fly. This disease occurs in 36 sub-Saharan Africa countries.
Human African trypanosomiasis is caused by protozoa of the species Trypanosoma brucei and transmitted by the tsetse fly. This disease occurs in 36 sub-Saharan Africa countries.
The disease progresses in two stages. In the first stage, trypanosomes multiply in subcutaneous tissues, blood and lymph; causing headaches, pain, and itching. In the second stage, the parasites cross the blood-brain barrier and infect the central nervous system. This causes confusion, poor coordination, and sensory and sleep-cycle disturbances.
Drugs administered in the first stage are less toxic and more effective. Drugs administered to second-stage patients are complicated to administer and have high levels of toxicity.
Source: World Health Organization
OUR FOCUS
CERID’s research on African Trypanosomiasis is focused on drug discovery & development.
Associated labs