This is unpublished
Overview
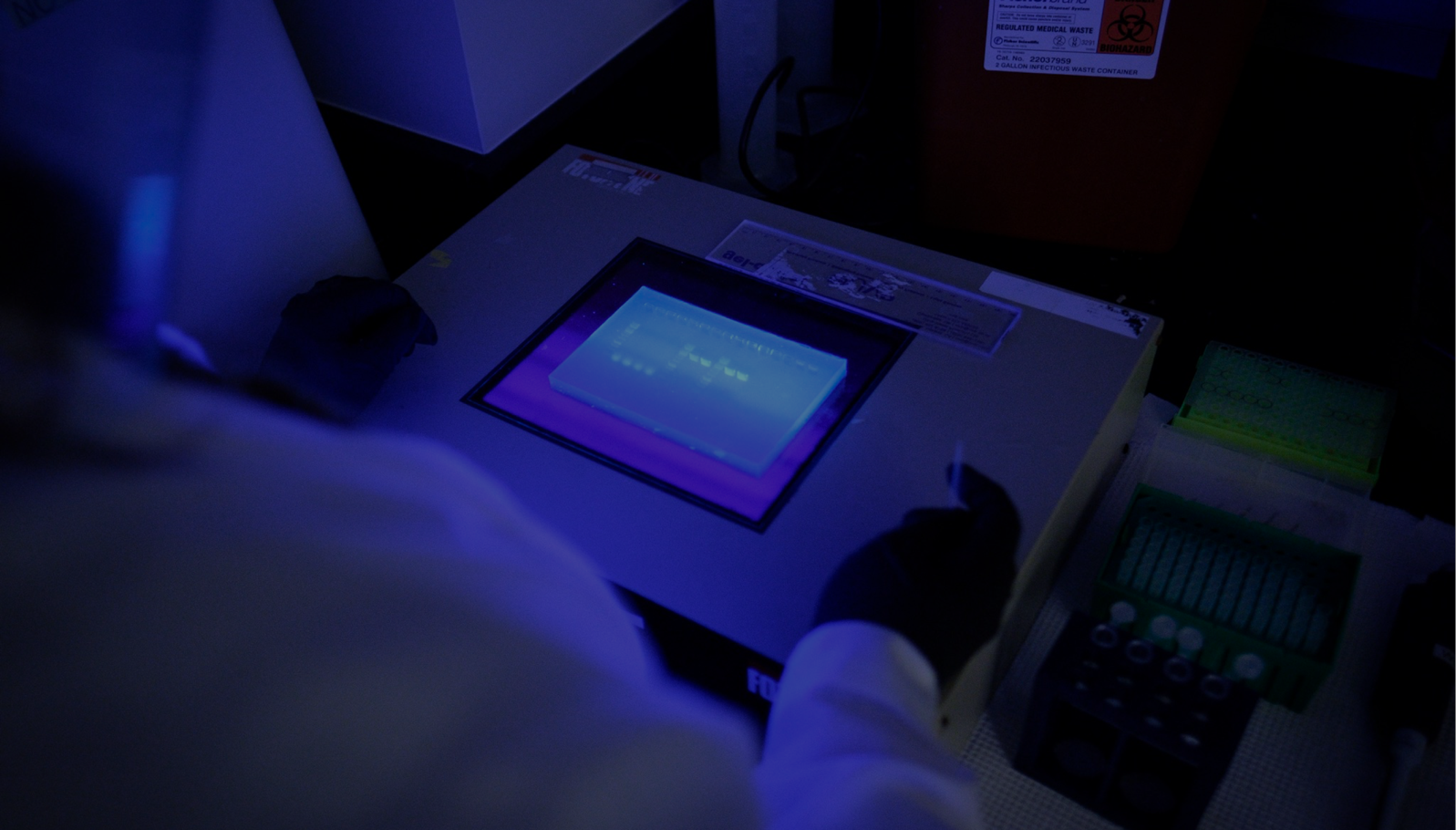
West Nile virus (WNV) was once only commonly found in Africa and the Middle East but it has now spread globally. WNV is now considered to be an endemic pathogen in Africa, Asia, Australia, the Middle East, Europe and the United States.
Human infection is most often the result of bites from infected mosquitoes. The infection is asymptomatic in approximately 80% of cases. 20% of cases will develop West Nile fever (headache, tiredness, body aches, nausea, skin rash), with a small percentage developing a severe form of the disease that can cause neurological symptoms and death.
Treatment often includes hospitalization, IV fluids, and respiratory support. There is no vaccine for WNV.
Source: World Health Organization
Associated labs